图像轮廓过滤思路
- 高斯降噪
- 转灰度
- 计算 X 梯度
- 计算 Y 梯度
- 合并梯度
一. Robert 算子
原理
- 对像素曲线的一阶求导
算子卷积核
- Sobel X 方向上的卷积核
- [ -1, 0,
0, 1]
- [ -1, 0,
- Sobel Y 方向上的卷积核
- [ 0, -1,
1, 0]
- [ 0, -1,
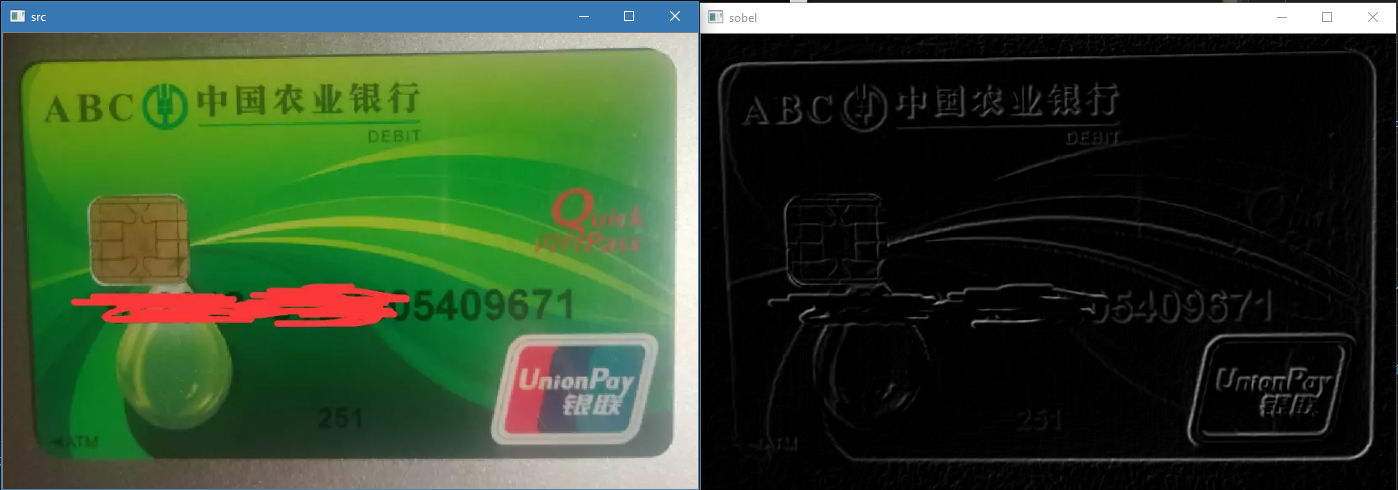
二. Sobel 算子
- 根据的 Robert 算子改造出来一个 3x3 模板, 即 Sobel 算子
- 是离散的一阶微分求导, 用于计算图像的梯度
算子的卷积核
- Sobel X 方向上的卷积核, 若锚点像素的上下像素的差值比较大, 则说明在水平方向上存在轮廓
- [ -1, -2, -1,
0, 0, 0,
1, 2, 1]
- [ -1, -2, -1,
- Sobel Y 方向上的卷积核, 若锚点像素的左右像素的差值比较大, 则说明在竖直方向上存在轮廓
- [ -1, 0, 1,
-2, 0, 2,
-1, 0, 1]
- [ -1, 0, 1,
卷积实现
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
void main() {
Mat src = imread("F:/VisualStudioSpace/OpenCV/Resource/card.jpg");
imshow("src", src);
// 降噪
Mat gussian;
GaussianBlur(src, gussian, Size(3, 3), 0);
// 灰度
Mat gray;
cvtColor(gussian, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
Mat sobel_x;
// 1. 定义 Sobel X 方向算子
Mat sobel_x_kernel = (Mat_<char>(3, 3) <<
-1, -2, -1,
0, 0, 0,
1, 2, 1
);
filter2D(gray, sobel_x, gray.depth(), sobel_x_kernel, Point(-1, -1));
// 2. 定义 Sobel Y 方向算子
Mat sobel_y;
Mat sobel_y_kernel = (Mat_<char>(3, 3) <<
-1, 0, 1,
-2, 0, 2,
-1, 0, 1
);
filter2D(gray, sobel_y, gray.depth(), sobel_y_kernel, Point(-1, -1));
// 3. 求绝对值
convertScaleAbs(sobel_x, sobel_x);
convertScaleAbs(sobel_y, sobel_y);
// 4. 合并 X, Y 梯度
Mat sobel;
addWeighted(sobel_x, 0.5, sobel_y, 0.5, 0, sobel);
imshow("sobel", sobel);
cvWaitKey(0);
}
OpenCV API
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
void main() {
Mat src = imread("F:/VisualStudioSpace/OpenCV/Resource/card.jpg");
imshow("src", src);
// 降噪
Mat gussian;
GaussianBlur(src, gussian, Size(3, 3), 0);
// 灰度
Mat gray;
cvtColor(gussian, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
// 1. 计算 X 轴向的梯度
Mat sobel_x;
Sobel(
gray,
sobel_x,
CV_16S, // 卷积核精度
1, // X 方向的梯度
0, // Y 方向的梯度
3, // 卷积核大小
1, // 在计算结果的基础上 * scale
0.0 // 在计算结果的基础上 + delta
);
imshow("sobel_x", sobel_x);
// 2. 计算 Y 轴向的梯度
Mat sobel_y;
Sobel(gray, sobel_y, CV_32F, 0, 1, 3);
imshow("sobel_y", sobel_y);
// 3. 求绝对值
convertScaleAbs(sobel_x, sobel_x);
convertScaleAbs(sobel_y, sobel_y);
// 4. 合并 X, Y 梯度
Mat sobel;
addWeighted(sobel_x, 0.5, sobel_y, 0.5, 0, sobel);
imshow("sobel", sobel);
cvWaitKey(0);
}

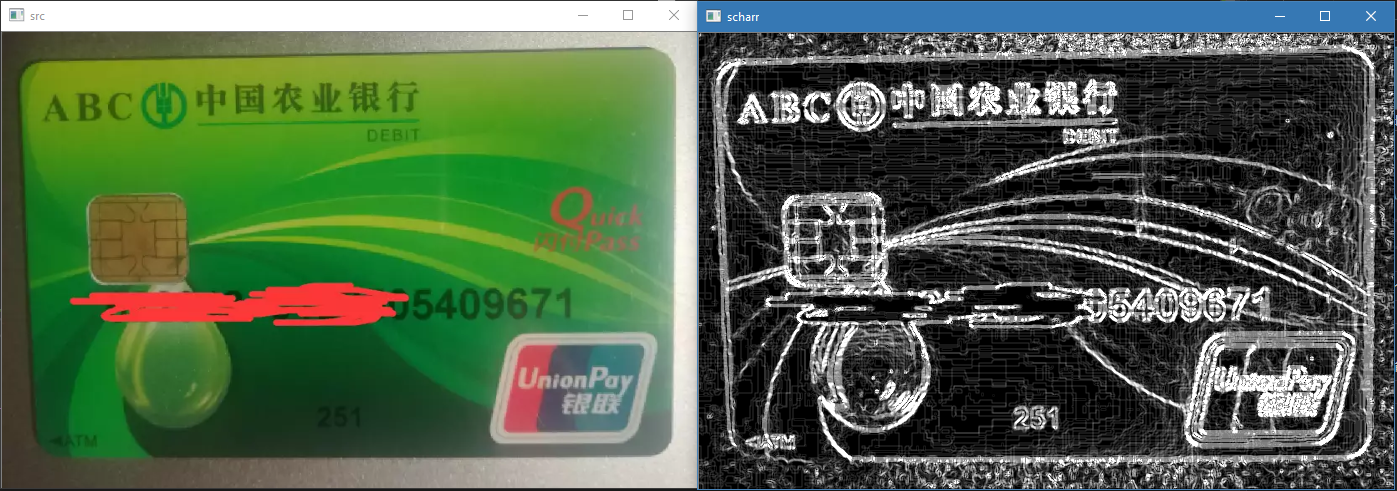
三. Scharr 算子
在 Sobel 上的增强, 效果最好, 速度稍慢
代码实现
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
void main() {
Mat src = imread("F:/VisualStudioSpace/OpenCV/Resource/card.jpg");
imshow("src", src);
// 降噪
Mat gussian;
GaussianBlur(src, gussian, Size(3, 3), 0);
// 先转为灰度
Mat gray;
cvtColor(gussian, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
// 1. 计算 X 轴向的梯度
Mat scharr_x;
Scharr(
gray,
scharr_x,
CV_16S, // 卷积核精度
1, // X 方向的梯度
0, // Y 方向的梯度
3 // 卷积核大小
);
// 2. 计算 Y 轴向的梯度
Mat scharr_y;
Scharr(gray, scharr_y, CV_16S, 0, 1, 3);
// 3. 求绝对值
convertScaleAbs(scharr_x, scharr_x);
convertScaleAbs(scharr_y, scharr_y);
// 4. 合并 X, Y 梯度
Mat scharr;
addWeighted(scharr_x, 0.5, scharr_y, 0.5, 0, scharr);
imshow("scharr", scharr);
cvWaitKey(0);
}