一. 什么是积分图(Integral Image)
积分图是一种在图像中快速计算矩形区域和的方法
二. 为什么要使用积分图?
我们知道在均值模糊操作时, 需要统计滑动窗口中所有像素的和然后取平均值
- 假设窗口大小为 w*w, 那么对于 n * m 的图片, 进行一次模糊操作, 其时间复杂度为 O(n * m * w * w)
在上述场景下, 若是使用积分图, 其时间复杂度便降低为 O(n * m * 1), 当滑动窗口比较大时, 这个提升是十分明显的
三. 积分图算法
创建积分图
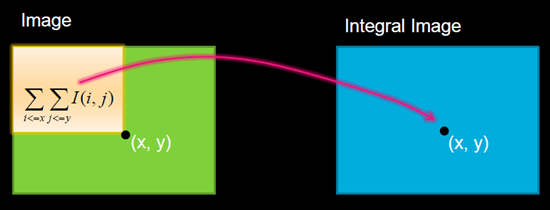
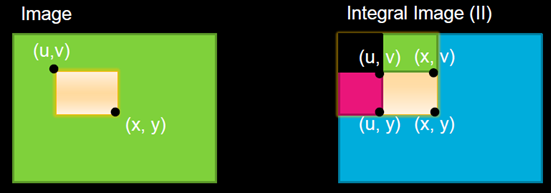
根据积分图求和
四. OpenCV 积分图的实现
OpenCV API
#include<iostream>
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
void main() {
Mat src = imread("F:/VisualStudioSpace/OpenCV/src/timg.jpg");
// 构建 src 的积分图
Mat sum_mat, sqsum_mat;
integral(
src, // 原图
sum_mat, // 输出的积分图
sqsum_mat, // 输出的积分平方图
CV_32S, // 积分图的数据单位
CV_32F // 积分平方图的数据单位
);
}
手动实现积分图
#include<iostream>
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
#define sqrt(num) num*num
void calIntegral(const Mat &src, Mat & sum, Mat & sqsum) {
int channels = src.channels();
// 构建积分图和平方图, 在 mat 的像素基础上拓展一行一列, 用于做边缘哨兵处理
Size size((src.cols + 1) * channels, src.rows + 1);
sum.create(size, CV_32S);
sqsum.create(size, CV_32F);
// 初始化 哨兵行 和 哨兵列
for (int i = 0; i < size.height; i++) {
for (int c_index = 0; c_index < channels; c_index++) {
sum.at<Vec3i>(i, 0)[c_index] = 0;
sqsum.at<Vec3f>(i, 0)[c_index] = 0;
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < size.width; j++) {
sum.at<int>(0, j) = 0;
sqsum.at<float>(0, j) = 0;
}
// 计算积分图和积分平方图
Vec3b cur_pixel;
Vec3i l, t, lt;
Vec3f sq_l, sq_t, sq_lt;
for (int row = 0; row < src.rows; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < src.cols; col++) {
cur_pixel = src.at<Vec3b>(row, col);
// 计算积分图
lt = sum.at<Vec3i>(row, col);
l = sum.at<Vec3i>(row + 1, col);
t = sum.at<Vec3i>(row, col + 1);
for (int c_index = 0; c_index < channels; c_index++) {
sum.at<Vec3i>(row + 1, col + 1)[c_index] = cur_pixel[c_index] + l[c_index] + t[c_index]
- lt[c_index];
}
// 计算积分平方图
sq_lt = sqsum.at<Vec3f>(row, col);
sq_l = sqsum.at<Vec3f>(row + 1, col);
sq_t = sqsum.at<Vec3f>(row, col + 1);
for (int c_index = 0; c_index < channels; c_index++) {
sqsum.at<Vec3f>(row + 1, col + 1)[c_index] = sqrt(cur_pixel[c_index]) + sq_l[c_index]
+ sq_t[c_index] - sq_lt[c_index];
}
}
}
}
五. 利用积分图进行均值模糊
#include<iostream>
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
#define sqrt(num) num*num
void calIntegral(const Mat &src, Mat & sum, Mat & sqsum) {
int channels = src.channels();
// 构建积分图和平方图, 在 mat 的像素基础上拓展一行一列, 用于做边缘哨兵处理
Size size((src.cols + 1) * channels, src.rows + 1);
sum.create(size, CV_32S);
sqsum.create(size, CV_32F);
// 初始化 哨兵行 和 哨兵列
for (int i = 0; i < size.height; i++) {
for (int c_index = 0; c_index < channels; c_index++) {
sum.at<Vec3i>(i, 0)[c_index] = 0;
sqsum.at<Vec3f>(i, 0)[c_index] = 0;
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < size.width; j++) {
sum.at<int>(0, j) = 0;
sqsum.at<float>(0, j) = 0;
}
// 计算积分图和积分平方图
Vec3b cur_pixel;
Vec3i l, t, lt;
Vec3f sq_l, sq_t, sq_lt;
for (int row = 0; row < src.rows; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < src.cols; col++) {
cur_pixel = src.at<Vec3b>(row, col);
lt = sum.at<Vec3i>(row, col);
l = sum.at<Vec3i>(row + 1, col);
t = sum.at<Vec3i>(row, col + 1);
for (int c_index = 0; c_index < channels; c_index++) {
sum.at<Vec3i>(row + 1, col + 1)[c_index] = cur_pixel[c_index] + l[c_index] + t[c_index]
- lt[c_index];
}
sq_lt = sqsum.at<Vec3f>(row, col);
sq_l = sqsum.at<Vec3f>(row + 1, col);
sq_t = sqsum.at<Vec3f>(row, col + 1);
for (int c_index = 0; c_index < channels; c_index++) {
sqsum.at<Vec3f>(row + 1, col + 1)[c_index] = sqrt(cur_pixel[c_index]) + sq_l[c_index]
+ sq_t[c_index] - sq_lt[c_index];
}
}
}
}
void myBlur(const Mat & src, Mat & dst, int size) {
// 根据卷积核大小, 为原图填充边框
Mat mat;
int border_size = size >> 1;
copyMakeBorder(src, mat, border_size, border_size, border_size, border_size, BORDER_DEFAULT);
// 构建积分图
Mat sum, sqsum;
calIntegral(mat, sum, sqsum);
// 进行模糊操作
dst.create(src.size(), src.type());
int x, y, u, v;
int area = size * size;
for (int row = 0; row < src.rows; row++) {
u = row;
x = u + size;
for (int col = 0; col < src.cols; col++) {
v = col;
y = v + size;
for (int c_index = 0; c_index < dst.channels(); c_index++) {
dst.at<Vec3b>(row, col)[c_index] = (sum.at<Vec3i>(x, y)[c_index] + sum.at<Vec3i>(u, v)[c_index] -
sum.at<Vec3i>(u, y)[c_index] - sum.at<Vec3i>(x, v)[c_index]) / area;
}
}
}
}
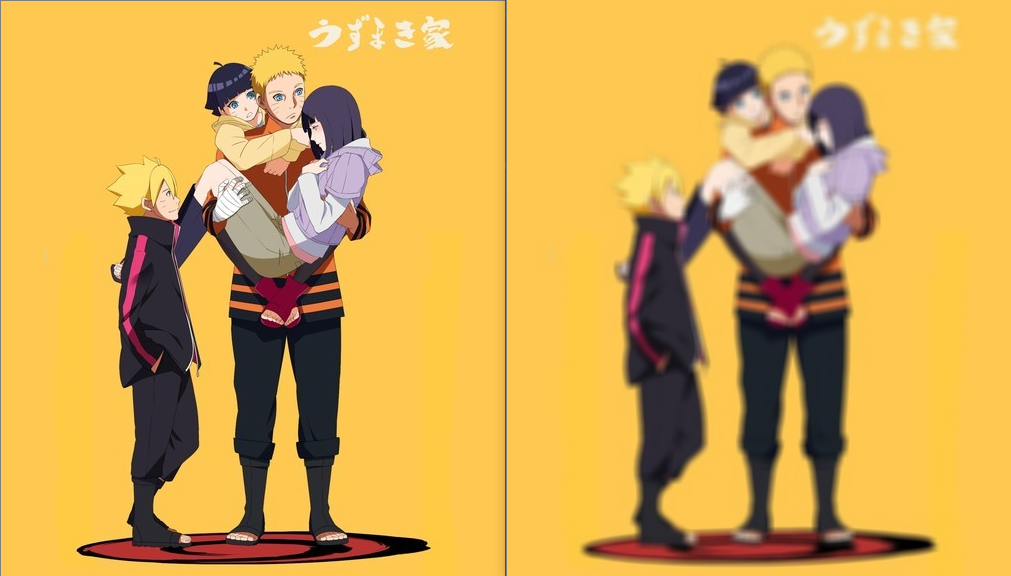
void main() {
Mat src = imread("F:/VisualStudioSpace/OpenCV/src/Naruto.png");
imshow("src", src);
Mat dst;
myBlur(src, dst, 9);
imshow("dst", dst);
waitKey(0);
}

总结
进行人像美容的过程中, 需要不同的算法结合才能达到预期的效果, 为了追求完美的用户体验, 即使是几毫秒的优化, 都是有必要去争取的, 有了积分图算法, 对于求和类的卷积运算的效率, 可以说是提升了一个量级, 不得不叹服前辈算法的奥妙