前言
我们知道 Glide 的图片框架是可以直接加载 GIF 图的, 笔者在监控项目内存使用的过程中, 发现 Gif 图过大时其内存消耗比较严重, 动画播放时伴随着稍许卡顿
这里我们系统的探究一下 Glide 的 GIF 加载原理和优化措施, 主要内容如下
- Glide 的 Gif 播放原理
- Glide 加载 GIF 卡顿探究
- Gif 加载的优化
一. Glide 的 Gif 播放原理
一) GIF 解码器的创建
public class StreamGifDecoder implements ResourceDecoder<InputStream, GifDrawable> {
private final List<ImageHeaderParser> parsers;
// ByteBufferGifDecoder
private final ResourceDecoder<ByteBuffer, GifDrawable> byteBufferDecoder;
private final ArrayPool byteArrayPool;
public StreamGifDecoder(List<ImageHeaderParser> parsers, ResourceDecoder<ByteBuffer,
GifDrawable> byteBufferDecoder, ArrayPool byteArrayPool) {
this.parsers = parsers;
this.byteBufferDecoder = byteBufferDecoder;
this.byteArrayPool = byteArrayPool;
}
@Override
public Resource<GifDrawable> decode(@NonNull InputStream source, int width, int height,
@NonNull Options options) throws IOException {
// 1. 使用 byte[] 来接收 InputStream
byte[] data = inputStreamToBytes(source);
if (data == null) {
return null;
}
// 2. 使用 ByteBuffer 包裹
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(data);
// 3. 将 GifDrawable 的创建转发到 ByteBufferGifDecoder 中
return byteBufferDecoder.decode(byteBuffer, width, height, options);
}
}
可以看到 Glide 拿到 Gif 的 InputStream 流时, 所做的操作如下
- 使用 byte[] 接收 InputStream
- 将 GIF 的 byte[] 数据交由 ByteBufferGifDecoder 处理
因此 ByteBufferGifDecoder 即为 InputStream 的解码实现, 我们看看它的 decode 操作
public class ByteBufferGifDecoder implements ResourceDecoder<ByteBuffer, GifDrawable> {
@Override
public GifDrawableResource decode(@NonNull ByteBuffer source, int width, int height,
@NonNull Options options) {
final GifHeaderParser parser = parserPool.obtain(source);
try {
// 执行 GIF 数据的 解码操作
return decode(source, width, height, parser, options);
} finally {
parserPool.release(parser);
}
}
@Nullable
private GifDrawableResource decode(
ByteBuffer byteBuffer, int width, int height, GifHeaderParser parser, Options options) {
long startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
try {
// 1. 获取 GIF 首部信息
final GifHeader header = parser.parseHeader();
if (header.getNumFrames() <= 0 || header.getStatus() != GifDecoder.STATUS_OK) {
// If we couldn't decode the GIF, we will end up with a frame count of 0.
return null;
}
// 2. 根据 GIF 背景是否有透明通道来选取 Bitmap 的类型
Bitmap.Config config = options.get(GifOptions.DECODE_FORMAT) == DecodeFormat.PREFER_RGB_565
? Bitmap.Config.RGB_565 : Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888;
// 3. 计算 Bitmap 的采样率
int sampleSize = getSampleSize(header, width, height);
// 4. 获取 Gif 数据的 StandardGifDecoder.
GifDecoder gifDecoder = gifDecoderFactory.build(provider, header, byteBuffer, sampleSize);
gifDecoder.setDefaultBitmapConfig(config);
gifDecoder.advance();
// 检验 GIF 是否有数据帧
Bitmap firstFrame = gifDecoder.getNextFrame();
if (firstFrame == null) {
return null;
}
Transformation<Bitmap> unitTransformation = UnitTransformation.get();
// 6. 构建 GIF 的 drawable
GifDrawable gifDrawable =
new GifDrawable(context, gifDecoder, unitTransformation, width, height, firstFrame);
// 7. 封装成 GifDrawableResource
return new GifDrawableResource(gifDrawable);
} finally {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "Decoded GIF from stream in " + LogTime.getElapsedMillis(startTime));
}
}
}
}
ByteBufferGifDecoder 的 decode 操作的流程还是很有趣的
- 获取 GIF 首部信息
- 获取 GIF 的背景色
- 计算采样率
- 获取 GIF 的解码器 StandardGifDecoder
- 构建 GifDrawable
- 构建 GifDrawableResource
其中我们需要重点关注的有, StandardGifDecoder 和 GifDrawable
- StandardGifDecoder: 用于解码 Gif 帧的数据到 Bitmap 中
- GifDrawable: 根据 GIF 帧与帧的间隔调度 GIF 帧的绘制
下面我们一一探索
二) Gif 图像帧的获取
通过 GifDecoder 的 getNextFrame 方法我们可以获取 GIF 下一帧的数据, 它的实现如下
public class StandardGifDecoder implements GifDecoder {
@Nullable
@Override
public synchronized Bitmap getNextFrame() {
......
// 根据 framePointer 获取 GIF 当前帧的描述
GifFrame currentFrame = header.frames.get(framePointer);
// 获取上一帧的描述
GifFrame previousFrame = null;
int previousIndex = framePointer - 1;
if (previousIndex >= 0) {
previousFrame = header.frames.get(previousIndex);
}
// 获取当前帧可用色表
// 优先取局部色表, 次优先取全局色表
act = currentFrame.lct != null ? currentFrame.lct : header.gct;
if (act == null) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "No valid color table found for frame #" + framePointer);
}
// No color table defined.
status = STATUS_FORMAT_ERROR;
return null;
}
// 重置透明像素
if (currentFrame.transparency) {
// Prepare local copy of color table ("pct = act"), see #1068
System.arraycopy(act, 0, pct, 0, act.length);
// Forget about act reference from shared header object, use copied version
act = pct;
// Set transparent color if specified.
act[currentFrame.transIndex] = COLOR_TRANSPARENT_BLACK;
}
// 解析当前帧的像素数据
return setPixels(currentFrame, previousFrame);
}
可以看到 StandardGifDecoder 获取下一帧的的方式如下
- 获取帧信息描述
- 获取色表, 若不存在局部色表, 则使用全局色表
- 读取当前帧的数据写入到 Bitmap 中
下面我们看看如何将 GIF 帧的数据注入到 Bitmap 中
public class StandardGifDecoder implements GifDecoder {
private Bitmap setPixels(GifFrame currentFrame, GifFrame previousFrame) {
// 存储上一帧的 Bitmap 像素数据
final int[] dest = mainScratch;
// 处理不需要上一帧的情况
if (previousFrame == null) {
// 回收上一帧的 Bitmap
if (previousImage != null) {
bitmapProvider.release(previousImage);
}
// 给 Bitmap 数组填充透明黑色
previousImage = null;
Arrays.fill(dest, COLOR_TRANSPARENT_BLACK);
}
// 上一帧的数据为 DISPOSAL_PREVIOUS 的, 清楚上一帧数据
if (previousFrame != null && previousFrame.dispose == DISPOSAL_PREVIOUS
&& previousImage == null) {
Arrays.fill(dest, COLOR_TRANSPARENT_BLACK);
}
// 1. 将上一帧的 Bitmap 数据注入到 dest 数组中
if (previousFrame != null && previousFrame.dispose > DISPOSAL_UNSPECIFIED) {
// We don't need to do anything for DISPOSAL_NONE, if it has the correct pixels so will our
// mainScratch and therefore so will our dest array.
if (previousFrame.dispose == DISPOSAL_BACKGROUND) {
// 填充背景色
@ColorInt int c = COLOR_TRANSPARENT_BLACK;
if (!currentFrame.transparency) {
c = header.bgColor;
if (currentFrame.lct != null && header.bgIndex == currentFrame.transIndex) {
c = COLOR_TRANSPARENT_BLACK;
}
} else if (framePointer == 0) {
// TODO: We should check and see if all individual pixels are replaced. If they are, the
// first frame isn't actually transparent. For now, it's simpler and safer to assume
// drawing a transparent background means the GIF contains transparency.
isFirstFrameTransparent = true;
}
// The area used by the graphic must be restored to the background color.
int downsampledIH = previousFrame.ih / sampleSize;
int downsampledIY = previousFrame.iy / sampleSize;
int downsampledIW = previousFrame.iw / sampleSize;
int downsampledIX = previousFrame.ix / sampleSize;
int topLeft = downsampledIY * downsampledWidth + downsampledIX;
int bottomLeft = topLeft + downsampledIH * downsampledWidth;
for (int left = topLeft; left < bottomLeft; left += downsampledWidth) {
int right = left + downsampledIW;
for (int pointer = left; pointer < right; pointer++) {
dest[pointer] = c;
}
}
} else if (previousFrame.dispose == DISPOSAL_PREVIOUS && previousImage != null) {
// 获取上一帧的 Bitmap 中的数据
previousImage.getPixels(dest, 0, downsampledWidth, 0, 0, downsampledWidth,
downsampledHeight);
}
}
// 2. 解析当前帧的数据到 dest 中
decodeBitmapData(currentFrame);
......
// 3. 获取到了当前帧的数据 dest, 将它更新到上一帧的 Bitmap 中暂存
if (savePrevious && (currentFrame.dispose == DISPOSAL_UNSPECIFIED
|| currentFrame.dispose == DISPOSAL_NONE)) {
if (previousImage == null) {
previousImage = getNextBitmap();
}
previousImage.setPixels(dest, 0, downsampledWidth, 0, 0, downsampledWidth,
downsampledHeight);
}
// 4. 获取新的 Bitmap, 将 dest 中的数据拷贝进去, 提供给外界使用
Bitmap result = getNextBitmap();
result.setPixels(dest, 0, downsampledWidth, 0, 0, downsampledWidth, downsampledHeight);
return result;
}
}
可以看到 StandardGifDecoder 将 GIF 的数据解析到 Bitmap 中需要做如下的操作
- 从上一帧的 Bitmap 中获取数据注入 dest 数组
- 解析当前帧的数据到 dest 数组
- 更新上一帧的 Bitmap 数据
- 获取新的 Bitmap, 将 dest 数组中的数据注入
StandardGifDecoder 每次获取新帧时主要做了如下两件事情
- 更新上一帧的 Bitmap 数据和上一帧的 int[] 数组
- 从复用池中获取的 Bitmap, 将数据拷贝后提供给外界使用
三) GifDrawable 播放 GIF 动画
public class GifDrawable extends Drawable implements GifFrameLoader.FrameCallback,
Animatable, Animatable2Compat {
......
private final GifState state;
public GifDrawable(
Context context,
GifDecoder gifDecoder,
Transformation<Bitmap> frameTransformation,
int targetFrameWidth,
int targetFrameHeight,
Bitmap firstFrame) {
this(
new GifState(
new GifFrameLoader(
// TODO(b/27524013): Factor out this call to Glide.get()
Glide.get(context),
gifDecoder,
targetFrameWidth,
targetFrameHeight,
frameTransformation,
firstFrame)));
}
GifDrawable(GifState state) {
this.state = Preconditions.checkNotNull(state);
}
}
其构造函数中构建一个 GifState 对象, 其内部由创建了 GifFrameLoader, 它是帮助 GifDrawable 调度 GIF 动画执行的封装类
从 GifDrawable 的接口实现中可知, 它是一个支持 Animatable 的 Drawable, 这就是为什么这个 Drawable 可以支持播放 GIF 动画的原因
接下来我们看看 GIF 动画是如何播放出来的
public class GifDrawable extends Drawable implements GifFrameLoader.FrameCallback,
Animatable, Animatable2Compat {
@Override
public void start() {
isStarted = true;
resetLoopCount();
if (isVisible) {
startRunning();
}
}
private void startRunning() {
......
if (state.frameLoader.getFrameCount() == 1) {
invalidateSelf();
} else if (!isRunning) {
isRunning = true;
// 1. 调用了 GifFrameLoader 的 subscribe 方法
state.frameLoader.subscribe(this);
invalidateSelf();
}
}
@Override
public void onFrameReady() {
......
// 2. 执行绘制
invalidateSelf();
......
}
}
GifDrawable 的 start 方法主要是将 GifDrawable 作为一个观察者注册到 GifFrameLoader 中
当 GifFrameLoader 需要绘制时, 会调用 onFrameReady 方法, 进而调用 invalidateSelf 执行当前帧的绘制 , 与此同时 subscribe 方法会触发 GifFrameLoader 绘制动作的调度
这里我们重点分析一下 GifFrameLoader 是如何调度 GifDrawable 执行 GIF 动画的绘制的
GifFrameLoader 调度动画的绘制
class GifFrameLoader {
void subscribe(FrameCallback frameCallback) {
......
// 根据观察者队列是否为空判断是否需要开启 GIF 绘制调度
boolean start = callbacks.isEmpty();
// 添加观察者
callbacks.add(frameCallback);
// 执行 GIF 绘制调度
if (start) {
start();
}
}
private void start() {
if (isRunning) {
return;
}
isRunning = true;
isCleared = false;
loadNextFrame();
}
private void loadNextFrame() {
......
// 若当前存在未绘制的帧数据, 则直接调用 onFrameReady 通知观察者绘制当前帧
if (pendingTarget != null) {
DelayTarget temp = pendingTarget;
pendingTarget = null;
onFrameReady(temp);
return;
}
// 获取下一帧要绘制的间隔时长
isLoadPending = true;
int delay = gifDecoder.getNextDelay();
long targetTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delay;
// 更新下一帧的位置
gifDecoder.advance();
// 创建一个 Delay 的消息
next = new DelayTarget(handler, gifDecoder.getCurrentFrameIndex(), targetTime);
// 再次执行 Glide 的流程, 在 targetTime 时, 执行数据帧的获取
requestBuilder.apply(signatureOf(getFrameSignature())).load(gifDecoder).into(next);
}
}
GifFrameLoader 的调度还是比较巧妙的, 它将 gifDecoder 作为要加载的数据源, DelayTarget 作为数据接收者, 执行了一次 Glide 的加载流程
有了 gifDecoder 又有了要解析的帧位置, 通过我们上面分析的 StandardGifDecoder 的 getNextFrame 就可以获取当前帧的 Bitmap 数据了
下面看看 DelayTarget 是如何回调让 GifDrawable 加载的
class GifFrameLoader {
GifFrameLoader(
BitmapPool bitmapPool,
RequestManager requestManager,
GifDecoder gifDecoder,
Handler handler,
RequestBuilder<Bitmap> requestBuilder,
Transformation<Bitmap> transformation,
Bitmap firstFrame) {
......
// 创建了主线程的 handler.
if (handler == null) {
handler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper(), new FrameLoaderCallback());
}
this.handler = handler;
......
}
static class DelayTarget extends SimpleTarget<Bitmap> {
private final Handler handler;
@Synthetic final int index;
private final long targetTime;
private Bitmap resource;
DelayTarget(Handler handler, int index, long targetTime) {
this.handler = handler;
this.index = index;
this.targetTime = targetTime;
}
Bitmap getResource() {
return resource;
}
@Override
public void onResourceReady(@NonNull Bitmap resource,
@Nullable Transition<? super Bitmap> transition) {
// GIF 下一帧的 Bitmap
this.resource = resource;
// 发送延时消息在指定的时刻执行帧的绘制操作
Message msg = handler.obtainMessage(FrameLoaderCallback.MSG_DELAY, this);
handler.sendMessageAtTime(msg, targetTime);
}
}
}
好的, 可以看到在 onResourceReady 中, 它通过 handler 将 FrameLoaderCallback.MSG_DELAY 消息在 targetTime 时刻投递到主线程的消息队列中执行, Handler 对于这个消息的处理如下
class GifFrameLoader {
private class FrameLoaderCallback implements Handler.Callback {
static final int MSG_DELAY = 1;
static final int MSG_CLEAR = 2;
@Synthetic
FrameLoaderCallback() { }
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.what == MSG_DELAY) {
// 回调了 onFrameReady 通知 GifDrawable 绘制
GifFrameLoader.DelayTarget target = (DelayTarget) msg.obj;
onFrameReady(target);
return true;
} else if (msg.what == MSG_CLEAR) {
......
}
return false;
}
}
@VisibleForTesting
void onFrameReady(DelayTarget delayTarget) {
......
if (delayTarget.getResource() != null) {
recycleFirstFrame();
DelayTarget previous = current;
current = delayTarget;
// 1. 回调观察者集合, 执行 GIF 当前帧的绘制
for (int i = callbacks.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
FrameCallback cb = callbacks.get(i);
cb.onFrameReady();
}
if (previous != null) {
handler.obtainMessage(FrameLoaderCallback.MSG_CLEAR, previous).sendToTarget();
}
}
// 2. 继续加载 GIF 的下一帧
loadNextFrame();
}
}
到这里对于 MSG_DELAY 消息的处理首先回调 GifDrawable 执行当前帧 Bitmap 的绘制, 然后调用 loadNextFrame 继续加载下一帧数据
至此 Glide 加载 Gif 动画的流程就完成了
四) 回顾
- 构建 Gif 的解码器
- 实现类为 StandardGifDecoder
- StandardGifDecoder 解码 Gif 帧
- 将当前帧的数据写入 dest 数组
- 更新上一帧 Bitmap
- 创建 Bitmap 返回到外界使用
- GifDrawable 播放 Gif 动画, 核心是使用 GifFrameLoader 调度动画的播放
- 通过 StandardGifDecoder 获取下一帧动画的 Bitmap
- 根据下一帧的间隔, 延时投递到主线程的消息队列中执行渲染
- 回调 GifDrawable 绘制获取到的 Bitmap
- 调用 loadNextFrame 继续加载下一帧动画的 Bitmap
思考
Glide 在使用 StandardGifDecoder 的过程中使用了很多缓存的技术, 在这里 BitmapPool 的作用就突出的淋漓尽致了, 但这并不意味着它是完美的, 仍然存在着如下的隐患
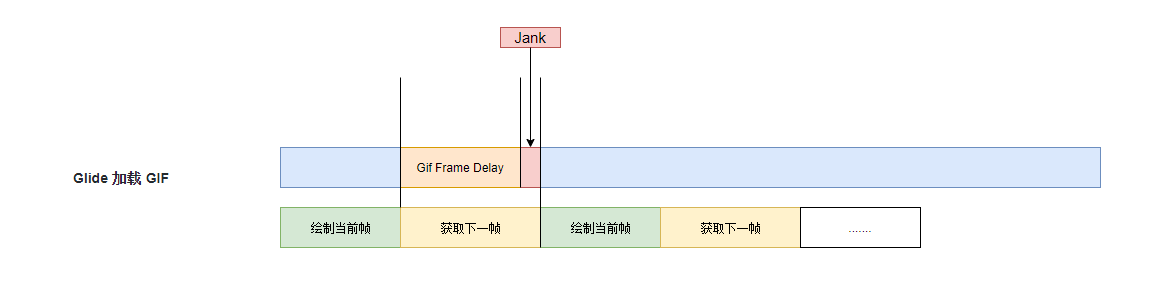
- 构建当前帧数据与准备下一帧是串行的
- 若是准备时长超过了 Gif 的 duration, 就会造成播放卡顿, CPU 使用率低, 可能会卡顿
- 内存消耗高
- StandardGifDecoder 只会保存上一帧的数据, 每次获取当前帧都会从 BitmapPool 中获取新的 Bitmap, 将数据拷贝进去之后再返回
- 也就是说加载一张 Gif 图, Glide 至少需要两个 Bitmap, BitmapPool 紧张时会创建更多
关于上述两点, Google 源码已经给出了很好的解决方案了, 它使用 Native 的 GIFLIB 引擎和 Java 层的 FrameSequenceDrawable 双缓冲机制解决了这个问题
下面看看具体的优化措施
二. Gif 加载的优化
一) GIFLIB 的编译
找到最新的版本, 可以看到其源码中并没有 CMakeLists.txt, 也没有 configure 文件, 这是非常不方便我们进行交叉编译的, 不过好在 Makefile 中我们可以看到那些文件是我们需要的
# 所需实现文件
SOURCES = dgif_lib.c egif_lib.c gifalloc.c gif_err.c gif_font.c \
gif_hash.c openbsd-reallocarray.c
# 所需头文件
HEADERS = gif_hash.h gif_lib.h gif_lib_private.h
OBJECTS = $(SOURCES:.c=.o)
USOURCES = qprintf.c quantize.c getarg.c
UHEADERS = getarg.h
UOBJECTS = $(USOURCES:.c=.o)
# 一些工具类, 可以通过这个工具类学习 GIFLIB 的使用
INSTALLABLE = \
gif2rgb \
gifbuild \
giffix \
giftext \
giftool \
gifclrmp
好的, 我们只需要将这些文件拷贝 AS 中就可以使用了, 工具类就不用拷贝了, 我们可以从 Google 的源码中学习其使用方式, 链接如下 http://androidxref.com/9.0.0_r3/xref/frameworks/ex/framesequence/jni/
二) 双缓冲的实现
Java 层的封装实现, 可以参考 FrameSequenceDrawable, 这里分析一下它的双缓冲机制
public class FrameSequenceDrawable extends Drawable implements Animatable, Runnable {
public FrameSequenceDrawable(FrameSequence frameSequence, BitmapProvider bitmapProvider) {
......
mFrameSequence = frameSequence;
mFrameSequenceState = frameSequence.createState();
final int width = frameSequence.getWidth();
final int height = frameSequence.getHeight();
mBitmapProvider = bitmapProvider;
// 前台绘制的 Bitmap
mFrontBitmap = acquireAndValidateBitmap(bitmapProvider, width, height);
// 后台获取下一帧的 Bitmap
mBackBitmap = acquireAndValidateBitmap(bitmapProvider, width, height);
......
// 启动 decode 线程, 用于处理后台解码 Gif 的任务
initializeDecodingThread();
}
}
从其构造函数中可以看到, 它创建了两个 Bitmap, 下面看看它的 start 是如何触发 Gif 动画的
1. 开启 Gif 动画调度
public class FrameSequenceDrawable extends Drawable implements Animatable, Runnable {
@Override
public void start() {
if (!isRunning()) {
synchronized (mLock) {
checkDestroyedLocked();
if (mState == STATE_SCHEDULED) {
return; // already scheduled
}
mCurrentLoop = 0;
// 执行一次解码操作
scheduleDecodeLocked();
}
}
}
private void scheduleDecodeLocked() {
mState = STATE_SCHEDULED;
mNextFrameToDecode = (mNextFrameToDecode + 1) % mDecoder.getFrameCount();
sDecodingThreadHandler.post(mDecodeRunnable);
}
private final Runnable mDecodeRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
int nextFrame;
Bitmap bitmap;
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mDestroyed) {
return;
}
nextFrame = mNextFrameToDecode;
if (nextFrame < 0) {
return;
}
bitmap = mBackBitmap;
mState = STATE_DECODING;
}
int lastFrame = nextFrame - 2;
boolean exceptionDuringDecode = false;
long invalidateTimeMs = 0;
try {
// 1. 解码下一帧
invalidateTimeMs = mDecoder.getFrame(nextFrame, bitmap, lastFrame);
} catch (Exception e) {
......
}
if (invalidateTimeMs < MIN_DELAY_MS) {
invalidateTimeMs = DEFAULT_DELAY_MS;
}
boolean schedule = false;
Bitmap bitmapToRelease = null;
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mDestroyed) {
bitmapToRelease = mBackBitmap;
mBackBitmap = null;
} else if (mNextFrameToDecode >= 0 && mState == STATE_DECODING) {
// 走到这里说明下一帧解码完成, 等待绘制
schedule = true;
mNextSwap = exceptionDuringDecode ? Long.MAX_VALUE : invalidateTimeMs + mLastSwap;
mState = STATE_WAITING_TO_SWAP;
}
}
if (schedule) {
// 2. 在 mNextSwap 时刻, 执行绘制流程
scheduleSelf(FrameSequenceDrawable.this, mNextSwap);
}
......
}
};
@Override
public void run() {
// set ready to swap as necessary
boolean invalidate = false;
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mNextFrameToDecode >= 0 && mState == STATE_WAITING_TO_SWAP) {
mState = STATE_READY_TO_SWAP;
invalidate = true;
}
}
if (invalidate) {
// 3. 绘制解码到的数据
invalidateSelf();
}
}
}
可以看到 start 方法会触发一次解码操作, 解码完成之后, 通过 scheduleSelf 在指定时刻执行绘制
到这里与 Glide 调度绘制几乎是一致的, 还没有看出双缓冲的作用, 下面我们去绘制流程中寻找答案
2. 执行绘制
public class FrameSequenceDrawable extends Drawable implements Animatable, Runnable {
@Override
public void draw(@NonNull Canvas canvas) {
synchronized (mLock) {
checkDestroyedLocked();
if (mState == STATE_WAITING_TO_SWAP) {
// may have failed to schedule mark ready runnable,
// so go ahead and swap if swapping is due
if (mNextSwap - SystemClock.uptimeMillis() <= 0) {
mState = STATE_READY_TO_SWAP;
}
}
if (isRunning() && mState == STATE_READY_TO_SWAP) {
// 1. 直接将 Decode 线程获取的 mBackBitmap 置换到 mFrontBitmap
Bitmap tmp = mBackBitmap;
mBackBitmap = mFrontBitmap;
mFrontBitmap = tmp;
.....
// 2. 通知 decode 线程执行下一次解码
if (continueLooping) {
scheduleDecodeLocked();
} else {
scheduleSelf(mFinishedCallbackRunnable, 0);
}
}
}
if (mCircleMaskEnabled) {
......
} else {
// 3. 绘制当前帧
mPaint.setShader(null);
canvas.drawBitmap(mFrontBitmap, mSrcRect, getBounds(), mPaint);
}
}
}
可以看到 FrameSequenceDrawable 的 draw 方法体现了双缓冲机制的价值, 它直接将后台获取到的 mBackBitmap 置换到 mFrontBitmap, 然后立即通知子线程获取下一帧数据, 可以近似的任务获取下一帧和绘制当前帧是同时进行的
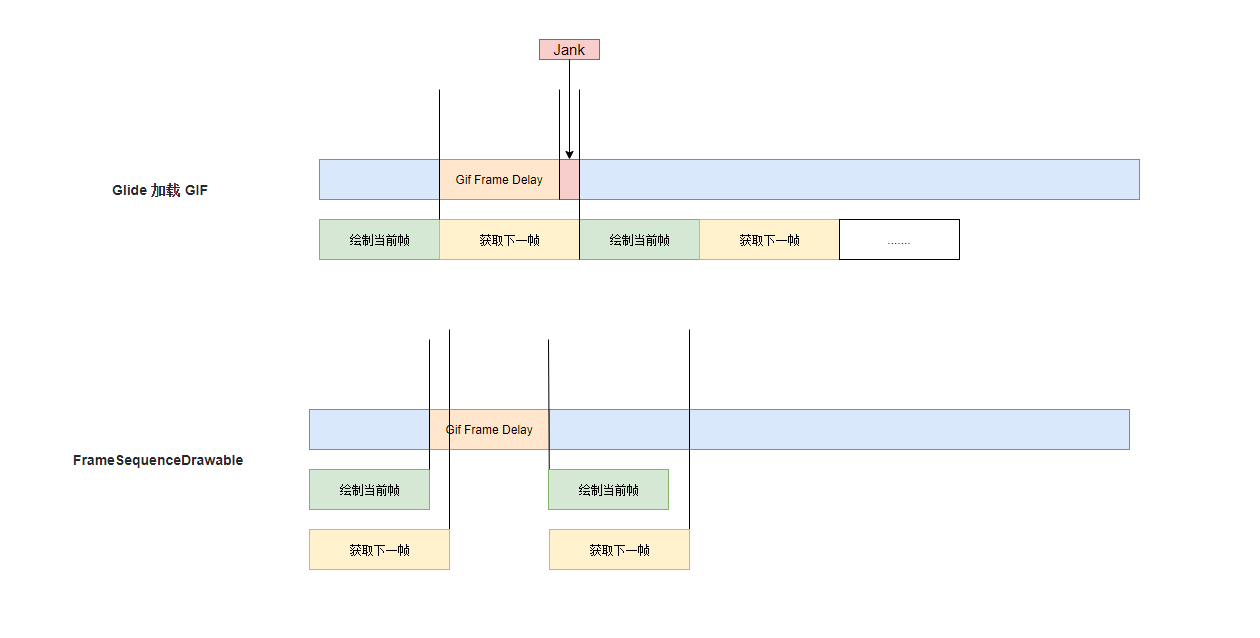
比起 Glide 的串行操作, FrameSequenceDrawable 显然对 CPU 时间片的利用更加充分
不过 FrameSequenceDrawable 虽好, 不过 Android 实现的 FrameSequenceDrawable 是不支持对 Bitmap 降采样的操作的, 也就是说它创建的 Bitmap 大小与 Gif 图大小是一致的, 若是 GIF 图尺寸过大, 超过了我们 View 的大小, 虽然只会加载两种 Bitmap, 还是会造成额外的内存消耗, 因此我们需要在其基础上进行自定义让其支持降采样
由于篇幅的原因, 这里就不贴出代码实现了, 若是感兴趣可以尝试自行实现, 文末会给出相关的 Demo
三) 对比
// GIF 的参数如下
Width=306, Height=640, IsOpaque=true, FrameCount=122, LooperCount=0, Duration=8540ms
1. Glide 原生加载


2. GIFLIB + FrameSequenceDrawable


四) 回顾
可以看到比起 Glide 原生加载方式, 我们的 Giflib + FrameSequenceDrawable 要更省内存, 其主要区别在于 Graphic 内存的消耗
虽然 Glide 的 StandardGifDecoder 使用 BitmapPool 作为 Bitmap 复用支撑, 但是当加载的 GIF 图较大时, 超过了 BitmapPool 剩余可用大小还是会直接创建 Bitmap 的, 因此这个问题在 Gif 尺寸较大时会暴露的更加明显
使用 GIFLIB + 双缓冲的实现, 无论在什么情况下都只会创建两个 Bitmap, 因此它的内存消耗是非常稳定的
总结
Glide 加载 Gif 的流程
- 构建 Gif 的解码器
- 实现类为 StandardGifDecoder
- StandardGifDecoder 解码 Gif 帧
- 更新上一帧的 Bitmap 数据和上一帧的 int[] 数组
- 从复用池中获取的 Bitmap, 将数据拷贝后提供给外界使用
- GifDrawable 播放 Gif 动画, 核心是使用 GifFrameLoader 调度动画的播放
- 通过 StandardGifDecoder 获取下一帧动画的 Bitmap
- 根据下一帧的间隔, 延时投递到主线程的消息队列中执行渲染
- 回调 GifDrawable 绘制获取到的 Bitmap
- 调用 loadNextFrame 继续加载下一帧动画的 Bitmap
Glide 加载 Gif 的隐患
- 构建当前帧数据与准备下一帧是串行的
- 若是准备时长超过了 Gif 的 duration, 就会造成播放卡顿, CPU 使用率低, 可能会卡顿
- 内存消耗高
- StandardGifDecoder 只会保存上一帧的数据, 每次获取当前帧都会从 BitmapPool 中获取新的 Bitmap, 将数据拷贝进去之后再返回
- 也就是说加载一张 Gif 图, Glide 至少需要两个 Bitmap, BitmapPool 紧张时会创建更多
优化策略
- Giflib 在 native 层解码 GIF
- FrameSequenceDrawable 使用双缓冲绘制 GIF 动画
- 仅需要两个 Bitmap
笔者这里在 Google 的 FrameSequenceDrawable 的基础上添加了 Downsample 的功能, 并提供了集成到 Glide 使用的示例
- Sample GiflibSample