前言
通过直方图的绘制可知, 通过统计的数据处理图像, 可以获取更好的动态效果, 那么直方均衡补偿就是对统计数据的一个很好地应用
一. 算法实现
- 直方图的统计
- 计算直方图中像素的概率
- 计算像素的累加概率
- 生成映射表
- 从映射表中查找数据
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
// 计算 mat 的直方图的统计
void calHist(const Mat &mat, Mat &hist) {
// 初始化 hist
hist.create(1, 256, CV_32S);
for (int i = 0; i < hist.cols; i++)
{
hist.at<int>(0, i) = 0;
}
// 统计 mat 中, 每一个像素值出现的次数
for (int row = 0; row < mat.rows; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < mat.cols; col++) {
int index = mat.at<uchar>(row, col);
hist.at<int>(0, index)++;
}
}
}
// 将 src 中的数据归一化到 [0, edge] 中
void normalize(const Mat &src, Mat dst, int edge) {
// 1. 统计最大值
float max_value = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < src.rows; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < src.cols; col++) {
int val = src.at<int>(row, col);
if (val > max_value) {
max_value = val;
}
}
}
cout << max_value << endl;
// 2. 计算最大值与边界的比率
float ratio = edge / max_value;
// 3. 将 src 中的数据, 归一化到 [0, edge] 中
dst.create(src.size(), src.type());
for (int row = 0; row < src.rows; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < src.cols; col++) {
dst.at<int>(row, col) = src.at<int>(row, col) * ratio;
}
}
}
// 绘制直方图
void drawHist(int draw_width, int draw_height, Mat hist) {
Mat hist_image(draw_height, draw_width, CV_8SC4, Scalar(255, 255, 255));
int paintWidth = draw_width / hist.cols;
for (int i = 1; i < hist.cols; i++) {
line(
hist_image,
Point((i - 1) * paintWidth, draw_height - hist.at<int>(i - 1)),
Point(i * paintWidth, draw_height - hist.at<int>(i)),
Scalar(255, 0, 0),
paintWidth,
LINE_AA
);
}
imshow("hist", hist_image);
}
// 1. 直方图的统计
// 2. 计算直方图中像素的概率
// 3. 生成映射表
// 4. 从映射表中查找数据
void equalizeHist(const Mat &src, Mat &dst) {
Mat hist;
// 1. 统计直方图 -> hist
calHist(src, hist);
// 2. 计算直方图中像素的累加概率
Mat prob_mat(hist.size(), CV_32FC1);
float total_pixels = src.cols * src.rows;
for (int i = 0; i < hist.cols; i++) {
float prob = hist.at<int>(0, i) / total_pixels;
prob_mat.at<float>(0, i) = prob;
}
// 3. 计算累加概率
float prob_sum = 0;// 累加概率
for (int i = 0; i < hist.cols; i++) {
prob_sum += prob_mat.at<float>(0, i);
prob_mat.at<float>(0, i) = prob_sum;
}
// 4. 通过概率生成像素值的直方映射表
Mat map(hist.size(), hist.type());
for (int i = 0; i < hist.cols; i++) {
float prob = prob_mat.at<float>(0, i);
map.at<int>(0, i) = prob * 255;
}
// 5. 从映射表中查找数据
dst.create(src.size(), src.type());
for (int row = 0; row < src.rows; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < src.cols; col++) {
int pixel = src.at<uchar>(row, col);
int map_pixel = map.at<int>(0, pixel);
dst.at<uchar>(row, col) = map_pixel;
}
}
}
void main() {
Mat src = imread("F:/VisualStudioSpace/OpenCV/src/Naruto.jpg");
// imshow("src", src);
// 获取灰度图
Mat gray;
cvtColor(src, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
imshow("gray", gray);
// 对灰度图进行直方均衡
Mat equalize_mat;
equalizeHist(gray, equalize_mat);
imshow("equalize_mat", equalize_mat);
cvWaitKey(0);
}
OpenCV API
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
void main() {
Mat src = imread("F:/VisualStudioSpace/OpenCV/Resource/Naruto.jpg");
if (!src.data) {
printf("Read data failed");
return;
}
imshow("src", src);
// 转灰度
Mat gray;
cvtColor(src, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
imshow("gray", gray);
// 直方均衡补偿
Mat dst;
equalizeHist(gray, dst);
imshow("equalize", dst);
cvWaitKey(0);
}
效果展示
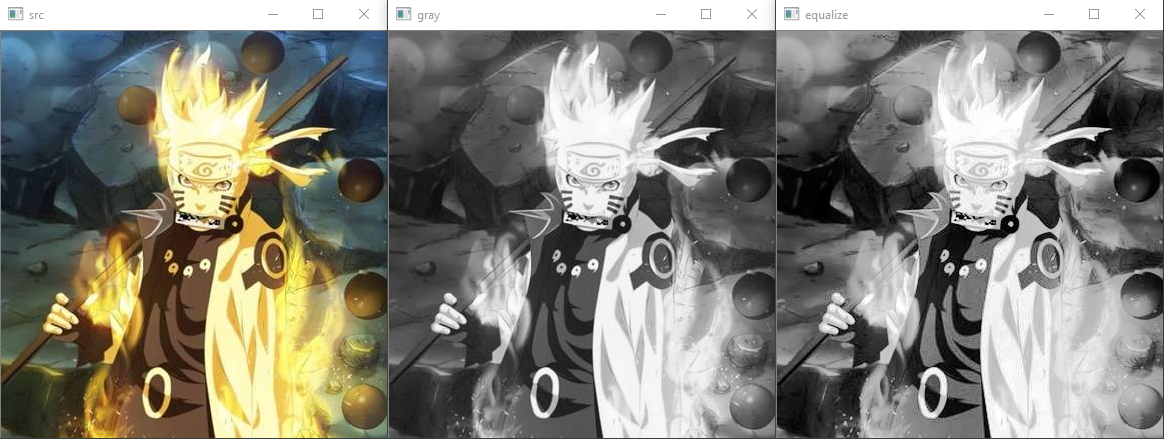
可以看到, 通过了直方均衡补偿之后, 图的颜色对比度更加的明显
二. 使用直方均衡美化图片
处理思路
- 获取指定通道的分量
- 使用直方均衡补偿操作该分量的数值
- 合入原图
操作代码
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<vector>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
void main() {
Mat src = imread("F:/VisualStudioSpace/OpenCV/Resource/equalize.jpg");
if (!src.data) {
printf("Read data failed");
return;
}
imshow("src", src);
// 1. 转 HSV
Mat hsv;
cvtColor(src, hsv, COLOR_BGR2HSV);
// 2. 提取 V 分量
vector<Mat> hsvs;
split(hsv, hsvs);
// 3. 对 V 分量进行直方均衡补偿
Mat equalize_v;
equalizeHist(hsvs[2], equalize_v);
// 4. 合入原图
// merge(equalize_v, hsv)
for (int i = 0; i < hsv.rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < hsv.cols; j++) {
hsv.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[2] = equalize_v.at<uchar>(i, j);
}
}
// 5. 转 BGR
Mat dst;
cvtColor(hsv, dst, COLOR_HSV2BGR);
imshow("equalized", dst);
cvWaitKey(0);
}
效果分析
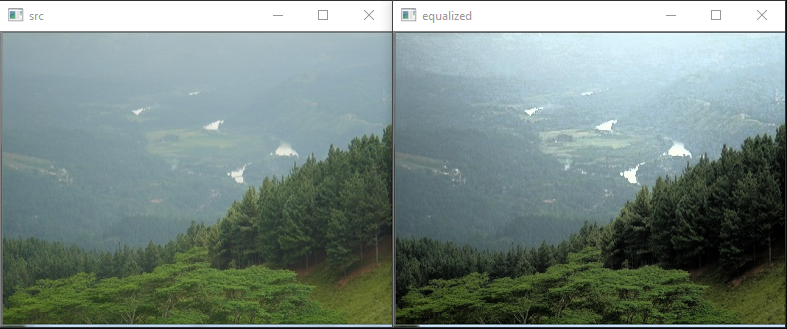
从图中效果可以看到, 处理后的图片其动态效果比起原图, 其对比度提升的比较明显, 图像观感更好