前言
通过前面的学习, 我们知道如何使用 GLSurfaceView 配合自定义 Renderer 来绘制我们想要的图像和纹理, 但却没有深究它是怎么工作的
这里我们通过 EGL 的学习来理清这一流程
什么是 EGL?
OpenGL ES 是操作 GPU 的 API, 它无法直接与屏幕设备进行交互, EGL 是 OpenGL ES 渲染 API 和本地窗口系统(native platform window system)之间的一个中间接口层,它也主要由厂商来实现
- EGLDisplay
- 显示设备抽象描述
- EGLContext
- 描述 OpenGL ES 的上下文, 存储 OpenGL ES绘图的一些状态信息
- EGLSurface
- 描述存储图像的内存缓冲区域, 在 Android 端为 Surface/SurfaceTexture
EGL 在 GLSurfaceView 中的使用
我们之前定义的 Renderer 能够在 GLSurfaceView 上执行渲染操作, 是因为 GLSurfaceView 中初始化了 EGL 的环境, 我们看看它是如何实现的
public class GLSurfaceView extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback2 {
private GLThread mGLThread;
private Renderer mRenderer;
public void setRenderer(Renderer renderer) {
......
mRenderer = renderer;
// 创建 GL 线程
mGLThread = newGLThread(mThisWeakRef);
// 启动 GL 线程
mGLThread.start();
}
}
好的, 可以看到在 GLSurfaceView.setRenderer 的方法中, 创建并启动了 GLThread 线程, 接下来看看具体实现
public class GLSurfaceView extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback2 {
static class GLThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
guardedRun();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
......
} finally {
......
}
}
private void guardedRun() throws InterruptedException {
mEglHelper = new EglHelper(mGLSurfaceViewWeakRef);
mHaveEglContext = false;
mHaveEglSurface = false;
mWantRenderNotification = false;
try {
GL10 gl = null;
boolean createEglContext = false;
boolean createEglSurface = false;
boolean createGlInterface = false;
boolean lostEglContext = false;
boolean sizeChanged = false;
while (true) {
synchronized (sGLThreadManager) {
while (true) {
if (mShouldExit) {
return;
}
......
// Ready to draw?
if (readyToDraw()) {
// If we don't have an EGL context, try to acquire one.
if (! mHaveEglContext) {
if (askedToReleaseEglContext) {
askedToReleaseEglContext = false;
} else {
try {
// 1. 初始化 GL 的环境
mEglHelper.start();
} catch (RuntimeException t) {
......
}
......
}
}
......
} else {
......
}
}
}
......
if (createEglSurface) {
// 2. 创建 GLSurface 描述帧缓冲
if (mEglHelper.createSurface()) {
......
} else {
......
continue;
}
createEglSurface = false;
}
......
// 3. 回调 Renderer 的生命周期
if (createEglContext) {
......
GLSurfaceView view = mGLSurfaceViewWeakRef.get();
if (view != null) {
try {
// 3.1 回调 onSurfaceCreated
view.mRenderer.onSurfaceCreated(gl, mEglHelper.mEglConfig);
} finally {
......
}
}
createEglContext = false;
}
if (sizeChanged) {
GLSurfaceView view = mGLSurfaceViewWeakRef.get();
if (view != null) {
try {
// 3.2 回调 onSurfaceChanged
view.mRenderer.onSurfaceChanged(gl, w, h);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
sizeChanged = false;
}
......
{
GLSurfaceView view = mGLSurfaceViewWeakRef.get();
if (view != null) {
try {
......
// 3.3 执行 onDrawFrame
view.mRenderer.onDrawFrame(gl);
......
} finally {
......
}
}
}
// 4. 将 EGLSurface 中的数据推入 SurfaceFlinger
int swapError = mEglHelper.swap();
......
}
} finally {
......
}
}
}
}
好的, 可以看到 GLThread 的 run 方法中启动了 guardedRun 方法, 其内部维护了一个死循环, 具体的流程如下
- 调用 mEglHelper.start 初始化 GL 的环境
- 调用 mEglHelper.createSurface 创建缓冲帧 EGLSurface
- 回调 Renderer 的生命周期了
- 调用 mEglHelper.swap 将 EGLSurface 中的数据推入 SurfaceFlinger
可以看到, 之所以我们的 Renderer 能够生效, 是因为在 GLSurfaceView 的 GLThread 线程中已经初始化了 EGL 的环境
EGL 的操作封装在了 EGLHelper 这个对象内部, 接下来我们一一分析这几个步骤
一. 创建 EGL 环境
public class GLSurfaceView extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback2 {
private static class EglHelper {
/**
* Initialize EGL for a given configuration spec.
* @param configSpec
*/
public void start() {
......
// 获取 EGL10 对象
mEgl = (EGL10) EGLContext.getEGL();
// 1. 创建 EGLDisplay 描述本地窗口的连接
mEglDisplay = mEgl.eglGetDisplay(EGL10.EGL_DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
......
// 1.2 初始化 EGLDisplay, 将版本号注入
int[] version = new int[2];
if(!mEgl.eglInitialize(mEglDisplay, version)) {
throw new RuntimeException("eglInitialize failed");
}
GLSurfaceView view = mGLSurfaceViewWeakRef.get();
if (view == null) {
mEglConfig = null;
mEglContext = null;
} else {
// 2. 创建 EGLConfig
mEglConfig = view.mEGLConfigChooser.chooseConfig(mEgl, mEglDisplay);
// 3. 创建 EGLContext
mEglContext = view.mEGLContextFactory.createContext(mEgl, mEglDisplay, mEglConfig);
}
......
mEglSurface = null;
}
}
}
可以看到 EglHelper.start 中的流程是非常清晰, 主要有三个步骤
- 创建 EGLDisplay 用于描述硬件屏幕
- 初始化 EGL, 获取主次版本号信息
- 创建 EGLConfig
- 创建 EGLContext
一) 创建 EGLDisplay
// frameworks/native/opengl/include/EGL/egl.h
typedef void *EGLConfig;
typedef void *EGLSurface;
typedef void *EGLContext;
// frameworks/native/opengl/libagl/egl.cpp
EGLDisplay eglGetDisplay(NativeDisplayType display)
{
......
if (display == EGL_DEFAULT_DISPLAY) {
EGLDisplay dpy = (EGLDisplay)1;
// 获取 EGLDisplay 对应的结构体 egl_display_t
egl_display_t& d = egl_display_t::get_display(dpy);
// 保存显示的类型
d.type = display;
// 返回 EGLDisplay
return dpy;
}
return EGL_NO_DISPLAY;
}
const unsigned int NUM_DISPLAYS = 1;
struct egl_display_t
{
NativeDisplayType type;
std::atomic_size_t initialized;
// 构造
egl_display_t() : type(0), initialized(0) { }
// 创建结构体
static egl_display_t& get_display(EGLDisplay dpy);
static EGLBoolean is_valid(EGLDisplay dpy) {
// DisplayType >= 1 说明 egl_display_t 有效
return ((uintptr_t(dpy)-1U) >= NUM_DISPLAYS) ? EGL_FALSE : EGL_TRUE;
}
};
好的, 可以看到 Native 层 EGLDisplay 是一个显示设备的标示符
- 当传入 EGL_DEFAULT_DISPLAY 时, 默认为 1
- EGLDisplay 对应了 egl_display_t 结构体
二) 创建 EGLConfig
public class GLSurfaceView extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback2 {
private EGLConfigChooser mEGLConfigChooser;
public void setRenderer(Renderer renderer) {
checkRenderThreadState();
if (mEGLConfigChooser == null) {
mEGLConfigChooser = new SimpleEGLConfigChooser(true);
}
}
private class SimpleEGLConfigChooser extends ComponentSizeChooser {
public SimpleEGLConfigChooser(boolean withDepthBuffer) {
super(8, 8, 8, 0, withDepthBuffer ? 16 : 0, 0);
}
}
/**
* Choose a configuration with exactly the specified r,g,b,a sizes,
* and at least the specified depth and stencil sizes.
*/
private class ComponentSizeChooser extends BaseConfigChooser {
public ComponentSizeChooser(int redSize, int greenSize, int blueSize,
int alphaSize, int depthSize, int stencilSize) {
super(
// 1. 定义 EGLConfig 配置数组
new int[] {
EGL10.EGL_RED_SIZE, redSize,
EGL10.EGL_GREEN_SIZE, greenSize,
EGL10.EGL_BLUE_SIZE, blueSize,
EGL10.EGL_ALPHA_SIZE, alphaSize,
EGL10.EGL_DEPTH_SIZE, depthSize,
EGL10.EGL_STENCIL_SIZE, stencilSize,
EGL10.EGL_NONE
}
);
......
}
......
}
private abstract class BaseConfigChooser
implements EGLConfigChooser {
protected int[] mConfigSpec;
public BaseConfigChooser(int[] configSpec) {
// 2. 过滤配置属性
mConfigSpec = filterConfigSpec(configSpec);
}
public EGLConfig chooseConfig(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display) {
// 3. 通过 EGL10.eglChooseConfig 获取符合配置的 EGLConfig 个数
int[] num_config = new int[1];
if (!egl.eglChooseConfig(display, mConfigSpec, null, 0,
num_config)) {
......
}
int numConfigs = num_config[0];
......
// 4. 通过 EGL10.eglChooseConfig 获取所有符合配置的 EGLConfig
EGLConfig[] configs = new EGLConfig[numConfigs];
if (!egl.eglChooseConfig(display, mConfigSpec, configs, numConfigs,
num_config)) {
......
}
// 5. 调用了抽象方法 chooseConfig, 一般选择 EGLConfig[] 第 0 个元素
EGLConfig config = chooseConfig(egl, display, configs);
if (config == null) {
......
}
return config;
}
}
}
可以看到这个 mEGLConfigChooser 的默认实现为 SimpleEGLConfigChooser 其具体的流程如下
- 定义 EGLConfig 配置数组
- 过滤配置数组
- 通过 EGL10.eglChooseConfig 获取符合配置的 EGLConfig 的个数
- 通过 EGL10.eglChooseConfig 获取所有符合配置的 EGLConfig
- 取所有符合配置的 EGLConfig 的首元素
有了 EGLConfig 之后便可以创建了 EGLContext 了
三) EGLContext 的创建
从上面的分析中可知, 创建 EGLContext 的动作由 mEGLContextFactory.createContext(…) 完成
public class GLSurfaceView extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback2 {
private class DefaultContextFactory implements EGLContextFactory {
private int EGL_CONTEXT_CLIENT_VERSION = 0x3098;
public EGLContext createContext(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display, EGLConfig config) {
int[] attrib_list = {EGL_CONTEXT_CLIENT_VERSION, mEGLContextClientVersion,
EGL10.EGL_NONE };
// 调用了 eglCreateContext 方法
return egl.eglCreateContext(display, config, EGL10.EGL_NO_CONTEXT,
mEGLContextClientVersion != 0 ? attrib_list : null);
}
}
}
下面看看 native 的实现
EGLContext eglCreateContext(EGLDisplay dpy, EGLConfig config,
EGLContext /*share_list*/, const EGLint* /*attrib_list*/)
{
// 验证 EGLDisplay 是否有效
if (egl_display_t::is_valid(dpy) == EGL_FALSE)
return setError(EGL_BAD_DISPLAY, EGL_NO_SURFACE);
// 创建 Native 层的 EGLContext
ogles_context_t* gl = ogles_init(sizeof(egl_context_t));
......
// 创建 egl_context_t 真正描述 egl 的上下文
egl_context_t* c = static_cast<egl_context_t*>(gl->rasterizer.base);
c->flags = egl_context_t::NEVER_CURRENT;
c->dpy = dpy;
c->config = config;
c->read = 0;
c->draw = 0;
// 强转成 EGLContext
return (EGLContext)gl;
}
好的, 可以看到创建 EGLContext 的过程与创建 EGLDisplay 一致, 它对应的结构体实现为 egl_context_t
至此当前线程的 EGL 的环境便搭建好了, 我们知道 OpenGL 绘制之后是需要输出的, 这个输出的缓冲区即为 EGLSurface, 接下来看看缓冲区的相关操作
二. 创建数据缓冲区
public class GLSurfaceView extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback2 {
private static class EglHelper {
public boolean createSurface() {
......
/*
* Create an EGL surface we can render into.
*/
GLSurfaceView view = mGLSurfaceViewWeakRef.get();
if (view != null) {
// 1. 调用 mEGLWindowSurfaceFactory.createWindowSurface 创建 EGLSurface
mEglSurface = view.mEGLWindowSurfaceFactory.createWindowSurface(mEgl,
mEglDisplay, mEglConfig, view.getHolder());
} else {
mEglSurface = null;
}
// 2. 将当前线程的 EGL 上下文设置为当前的 mEglContext
if (!mEgl.eglMakeCurrent(mEglDisplay, mEglSurface, mEglSurface, mEglContext)) {
......
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
}
可以看到 EglHelper.createSurface 中主要有两步操作
- 创建 EGLSurface
- 调用 EGL10.eglMakeCurrent 切换上下文
- 上下文切换成功之后, 当前线程便可以在该上下文下执行 OpenGL ES 的 API 了
我们先看看 EGLSurface 的创建
一) EGLSurface 的创建
public class GLSurfaceView extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback2 {
public void setRenderer(Renderer renderer) {
checkRenderThreadState();
......
if (mEGLWindowSurfaceFactory == null) {
mEGLWindowSurfaceFactory = new DefaultWindowSurfaceFactory();
}
......
}
private static class DefaultWindowSurfaceFactory implements EGLWindowSurfaceFactory {
public EGLSurface createWindowSurface(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display,
EGLConfig config, Object nativeWindow) {
EGLSurface result = null;
try {
// 调用了 EGL10.eglCreateWindowSurface 创建了 EGLSurface
result = egl.eglCreateWindowSurface(display, config, nativeWindow, null);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
......
}
return result;
}
}
}
可以看到这里调用了一个 EGL10.eglCreateWindowSurface 创建了一个 EGLSurface 对象, 接下来看看 native 的实现
EGLSurface eglCreateWindowSurface( EGLDisplay dpy, EGLConfig config,
NativeWindowType window,
const EGLint *attrib_list)
{
return createWindowSurface(dpy, config, window, attrib_list);
}
static EGLSurface createWindowSurface(EGLDisplay dpy, EGLConfig config,
NativeWindowType window, const EGLint* /*attrib_list*/)
{
// 验证 EGLDisplay 是否有效
if (egl_display_t::is_valid(dpy) == EGL_FALSE)
return setError(EGL_BAD_DISPLAY, EGL_NO_SURFACE);
......
// 创建 egl_surface_t
egl_surface_t* surface;
surface = new egl_window_surface_v2_t(dpy, config, depthFormat,
static_cast<ANativeWindow*>(window));
......
return surface;
}
struct egl_surface_t
{
enum {
PAGE_FLIP = 0x00000001,
MAGIC = 0x31415265
};
uint32_t magic;
EGLDisplay dpy;
EGLConfig config;
EGLContext ctx;
......
}
struct egl_window_surface_v2_t : public egl_surface_t
{
egl_window_surface_v2_t(
EGLDisplay dpy, EGLConfig config,
int32_t depthFormat,
ANativeWindow* window);
private:
ANativeWindow* nativeWindow;
ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer;
ANativeWindowBuffer* previousBuffer;
int width;
int height;
void* bits;
GGLFormat const* pixelFormatTable;
......
}
egl_window_surface_v2_t::egl_window_surface_v2_t(EGLDisplay dpy,
EGLConfig config,
int32_t depthFormat,
ANativeWindow* window)
: egl_surface_t(dpy, config, depthFormat),
nativeWindow(window), buffer(0), previousBuffer(0), bits(NULL)
{
......
}
好的, 我们看到 Native 层创建了一个 egl_surface_t 对象, 它的实现结构体为 egl_window_surface_v2_t, 它与 Surface/SurfaceTexture 对应
至此我们创建了一个用于保存 OpenGL 渲染管线输出数据的缓冲区, 接下来需要将其绑定到当前线程的 EGLContext, 才能正常工作, 我们看看 eglMakeCurrent 函数的实现
二) EGLSurface 绑定 EGLContext
EGLBoolean eglMakeCurrent( EGLDisplay dpy, EGLSurface draw,
EGLSurface read, EGLContext ctx)
{
......// 验证异常信息
// 获取当前线程上下文
GLContext current_ctx = EGL_NO_CONTEXT;
if (ctx == EGL_NO_CONTEXT) {
// if we're detaching, we need the current context
current_ctx = (EGLContext)getGlThreadSpecific();
}
// 将传入的上下文置为当前线程的上下文
ogles_context_t* gl = (ogles_context_t*)ctx;
if (makeCurrent(gl) == 0) {
if (ctx) {
......// 处理 EGLSurface 与新的上下文绑定
} else {
......// 处理 EGLSurface 与上下文的解绑
}
return EGL_TRUE;
}
return setError(EGL_BAD_ACCESS, EGL_FALSE);
}
static int makeCurrent(ogles_context_t* gl)
{
// 之前的上下文
ogles_context_t* current = (ogles_context_t*)getGlThreadSpecific();
if (gl) {
// 传入的上下文
egl_context_t* c = egl_context_t::context(gl);
// 若传入的上下文已经标记为当前上下文
if (c->flags & egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT) {
// 当前上下文与之不等, 这说明我们传入的 c 绑定的是其他线程的上下文
if (current != gl) {
return -1;
}
} else {
// 解除当前线程绑定的上下文
if (current) {
// mark the current context as not current, and flush
glFlush();
egl_context_t::context(current)->flags &= ~egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT;
}
}
// 将传入的 c 置为当前线程的上下文
if (!(c->flags & egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT)) {
setGlThreadSpecific(gl);
c->flags |= egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT;
}
} else {
// 若 gl 为 null, 则意为取消当前线程上下文的绑定
if (current) {
glFlush();
egl_context_t::context(current)->flags &= ~egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT;
}
// this thread has no context attached to it
setGlThreadSpecific(0);
}
return 0;
}
好的, 可以看到 makeCurrent 切换 OpenGL 渲染线程的上下文操作还是比较复杂的
- 传入 EGLContext 为无效, 则表示清空当前线程的上下文
- EGLSurface 会与之解绑
- 传入的 EGLContext 有效, 则将其置为当前线程的上下文
- 若 EGLContext 已绑定为其他线程的上下文, 会爆出异常
- 更新 EGLSurface 绑定的上下文
现在 EGLSurface 与 EGLContext 已经绑定好了, 现在就可以安心的执行 OpenGL 的渲染管线了, 也就是我们业务代码的编写
业务代码编写完成之后, 需要将数据推送到 SurfaceFlinger, 这就需要调用 eglSwapBuffers 来推送数据
三. 通知数据更新
public class GLSurfaceView extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback2 {
private static class EglHelper {
public int swap() {
// 调用了 EGL10.eglSwapBuffers, 将 mEglSurface 中的数据推送给到 SurfaceFlinger
if (!mEgl.eglSwapBuffers(mEglDisplay, mEglSurface)) {
return mEgl.eglGetError();
}
return EGL10.EGL_SUCCESS;
}
}
}
置换数据的操作很简单, 调用了 EGL10.eglSwapBuffers, 我们看看它的实现
EGLBoolean eglSwapBuffers(EGLDisplay dpy, EGLSurface draw)
{
// 验证 Display 是否有效
if (egl_display_t::is_valid(dpy) == EGL_FALSE)
return setError(EGL_BAD_DISPLAY, EGL_FALSE);
// 获取 EGLSurface 对应的结构体 egl_surface_t
egl_surface_t* d = static_cast<egl_surface_t*>(draw);
......
// 调用 egl_surface_t 的 swapBuffers
d->swapBuffers();
......
return EGL_TRUE;
}
可以看到, 这里调用了 egl_surface_t 的 swapBuffers 函数, 在 EGLSurface 创建的时候, 我们知道它的实现类为 egl_window_surface_v2_t, 因此我们看看 egl_window_surface_v2_t 的 swapBuffers 的实现
EGLBoolean egl_window_surface_v2_t::swapBuffers()
{
// 上面执行了渲染管线, 因此这里的 buffer 非 0
if (!buffer) {
return setError(EGL_BAD_ACCESS, EGL_FALSE);
}
// 1. 从上一次重绘区域上拷贝数据
if (!dirtyRegion.isEmpty()) {
dirtyRegion.andSelf(Rect(buffer->width, buffer->height));
if (previousBuffer) {
// 判断是否需要从上一次重绘区域上取数据
Region copyBack(Region::subtract(oldDirtyRegion, dirtyRegion));
if (!copyBack.isEmpty()) {
// 从上一帧的缓冲区取数据, 覆盖到 buffer 中
void* prevBits;
if (lock(previousBuffer,
GRALLOC_USAGE_SW_READ_OFTEN, &prevBits) == NO_ERROR) {
// copy from previousBuffer to buffer
copyBlt(buffer, bits, previousBuffer, prevBits, copyBack);
unlock(previousBuffer);
}
}
}
// 更新被重绘的区域
oldDirtyRegion = dirtyRegion;
}
if (previousBuffer) {
previousBuffer->common.decRef(&previousBuffer->common);
previousBuffer = 0;
}
// 走到这里, 说明对 buffer 的操作已经完成了, 释放锁定
unlock(buffer);
// 将其置为上一帧数据
previousBuffer = buffer;
// 2. 使用 nativeWindow 将这个缓冲区到 SurfaceFlinger 待绘制队列
nativeWindow->queueBuffer(nativeWindow, buffer, -1);
buffer = 0;
// 3. 获取一个新的缓冲区, 保存到 buffer 中
int fenceFd = -1;
if (nativeWindow->dequeueBuffer(nativeWindow, &buffer, &fenceFd) == NO_ERROR) {
// 获取用存储栅格化数据共享内存的内存文件描述符
sp<Fence> fence(new Fence(fenceFd));
// 等待缓冲区内存分配完毕
if (fence->wait(Fence::TIMEOUT_NEVER) != NO_ERROR) {
nativeWindow->cancelBuffer(nativeWindow, buffer, fenceFd);
return setError(EGL_BAD_ALLOC, EGL_FALSE);
}
......
// reallocate the depth-buffer if needed
if ((width != buffer->width) || (height != buffer->height)) {
// TODO: we probably should reset the swap rect here
// if the window size has changed
width = buffer->width;
height = buffer->height;
if (depth.data) {
free(depth.data);
depth.width = width;
depth.height = height;
depth.stride = buffer->stride;
uint64_t allocSize = static_cast<uint64_t>(depth.stride) *
static_cast<uint64_t>(depth.height) * 2;
if (depth.stride < 0 || depth.height > INT_MAX ||
allocSize > UINT32_MAX) {
setError(EGL_BAD_ALLOC, EGL_FALSE);
return EGL_FALSE;
}
depth.data = (GGLubyte*)malloc(allocSize);
if (depth.data == 0) {
setError(EGL_BAD_ALLOC, EGL_FALSE);
return EGL_FALSE;
}
}
}
......
} else {
return setError(EGL_BAD_CURRENT_SURFACE, EGL_FALSE);
}
return EGL_TRUE;
}
可以看到这里的 swapBuffers 的主要任务, 即将绘制到 Buffer 中的数据, 推送到 SurfaceFlinger 的渲染队列, 其主要步骤如下
- 从上一次重绘区域上拷贝数据
- 使用 nativeWindow(Surface/SurfaceTexture) 将这个缓冲区到 SurfaceFlinger 进程的 Layer 队列中
- 获取一个新的缓冲区, 保存到 buffer 中
四. EGL 的销毁
前面介绍了 GLSurfaceView 渲染线程 EGL 环境的创建相关的流程, 相对的, 当线程执行完毕, 我们还需要及时的释放 EGL 占用的资源
GLSurfaceView 中对于释放资源的代码比较分散, 这里就不以 GLSurfaceView 举例了, 它们的操作如下
public void release() {
if (mEGLDisplay != EGL10.EGL_NO_DISPLAY) {
EGL.eglMakeCurrent(mEGLDisplay, EGL10.EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL10.EGL_NO_SURFACE,
EGL10.EGL_NO_CONTEXT);
EGL.eglDestroyContext(mEGLDisplay, mEGLContext);
EGL.eglDestroySurface(mEGLDisplay, mEGLSurface);
EGL.eglTerminate(mEGLDisplay);
}
mEGLContext = EGL10.EGL_NO_CONTEXT;
mEGLDisplay = EGL10.EGL_NO_DISPLAY;
mEGLSurface = EGL10.EGL_NO_SURFACE;
mEGLConfig = null;
}
释放的操作比较简单, 这里就不再进入 native 查看了
总结
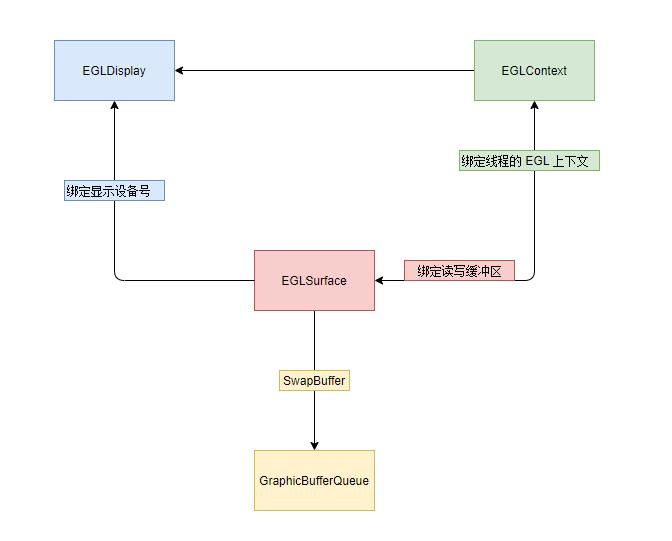
通过对 GLSurfaceView 中 EGL 分析, 我们得知 EGL 的使用流程如下所示
- 初始化环境
- 创建屏幕的描述 EGLDisplay(egl_display_t)
- 初始化 EGL 方法, 获取 EGL 版本号相关信息
- 创建 EGL 配置信息 EGLConfig(egl_config_t)
- 创建 EGL 上下文 EGLContext(egl_context_t)
- 创建缓冲帧 EGLSurface(egl_surface_t)
- 在线程中使用 EGL
- 通过 eglMakeCurrent 为当前线程绑定 EGLContext
- /////////////////////////////////////////
- 执行 OpenGL ES 的渲染管线
- /////////////////////////////////////////
- 交换缓冲, 将 EGLSurface 中的数据推送到 SurfaceFlinger 进程对应的 Layer 对象的队列中
- 推送之后, 会立即获取一个新的缓冲
- 绘制结束后销毁当前线程的 EGL 数据
掌握了这个流程, 我们可以封装一套 EGL 通用的代码(Google 示例), 便于在更多的场景下创建 EGL, 使用 OpenGL ES 的 API
- 感兴趣的同学可以仿照 GLSurfaceView 实现一个 GLTextureView